-
StatusOngoing
-
Status date2020-02-26
-
Activity Code6B.061
Next Generation Very High Throughput Satellites (VHTS) are now being deployed and provide capability to maximize the use of spectrum resources while offering high quality services at very competitive prices.
VHTS are transforming the industry in various aspects. After the innovation of on-board equipment, ground equipment , as MCC, need to keep the innovation pace.
As payloads are more and more complex and flexible, their management system becomes a key issue.
SpaceOps, TAS MCC Product Line, is a comprehensive Satellite management solution based on a modular architecture allowing to propose an integrated solution unifying all or parts of the functions of the needed mission segment :
- Mission planning
- Payload configuration and monitoring
- Spectrum and communications monitoring
- Interference / jamming management
- Mission supervision
- System Dynamic Resource Management
This ESA cofounded project allows the development of some SpaceOps critical features,

To occupy a dominant position on the Satcom market, Thales Alenia Space needs to keep on improving its MCC product line, expanding its functions accordingly to Satcom Operators expectations and constantly innovating to differentiate from competitors.
Thales Alenia Space objectives are extremely ambitious, with the development of some SpaceOps major and complex features (satellite fleet, flexibility, mobility, Q/V band and site diversity, dynamic resources management…) to enhance this product line and improve customer experience.
But these evolutions face the double challenge of requiring to be developed and made available at the right time but also with the right features to meet the market demand at best.
SpaceOps is designed, to ease Satcom operations, which are becoming more and more complex with the increasing complexity of the new flexible and highly capacitive Telecom Payloads.
It’s main expected benefits for Satcom Operators are:
- optimize the Satellite capacity for the best service quality to the largest number of the Satcom system end users
- plan coherently and optimize ground and payload resources in a multi-satellites context
- maximize Operators revenues
- Orchestrate efficiently & quickly changes to meet timely communication services requested
- Provide real-time supervision of communication services
- Prevent and / or react quickly to a malfunction.
In order to anticipate at best market evolution, the SpaceOps roadmap is organized according to 4 main axis:
- VHTS, flexibility, site diversity, mobility & dynamicity
- Fleet of satellites
- Advanced digital & processed payload
- 5G
The current project aims at developing features for the first of these axis (VHTS, flexibility, site diversity) for which TAS target a market availability by 2 to 3 years.
Thales Alenia Space, relying on its end-to-end system design experience, aims at developing and validating the following new features for its SpaceOps product:
- Capacity allocation algorithms opening & tuning : Link budget optimization model is different for commercial (statistical capacity assessment) and military (guaranteed capacity) contexts.
- PCM-Hilink interface: for using a high data rate link to reconfigure frequently the on-board Digital Transparent Processor.
- Site Diversity and Q/V band management: to improve Feeder links availabilities, especially when using Q/V bands, very sensitive to weather conditions/
- Flexibility management (DTP 5G & time tagged configuration): DTP5G offers the capability to save many configurations on board. Mechanisms to load a specific configuration shall be managed at ground level.
- MCC-NMS interface based on REST/JSON standards: Interface based on standard up to date protocol to facilitate integration in customer architecture
- MCC Security at an enhanced level: Cybersecurity shall be considered at system segment level. It includes the mission segment sub-system.
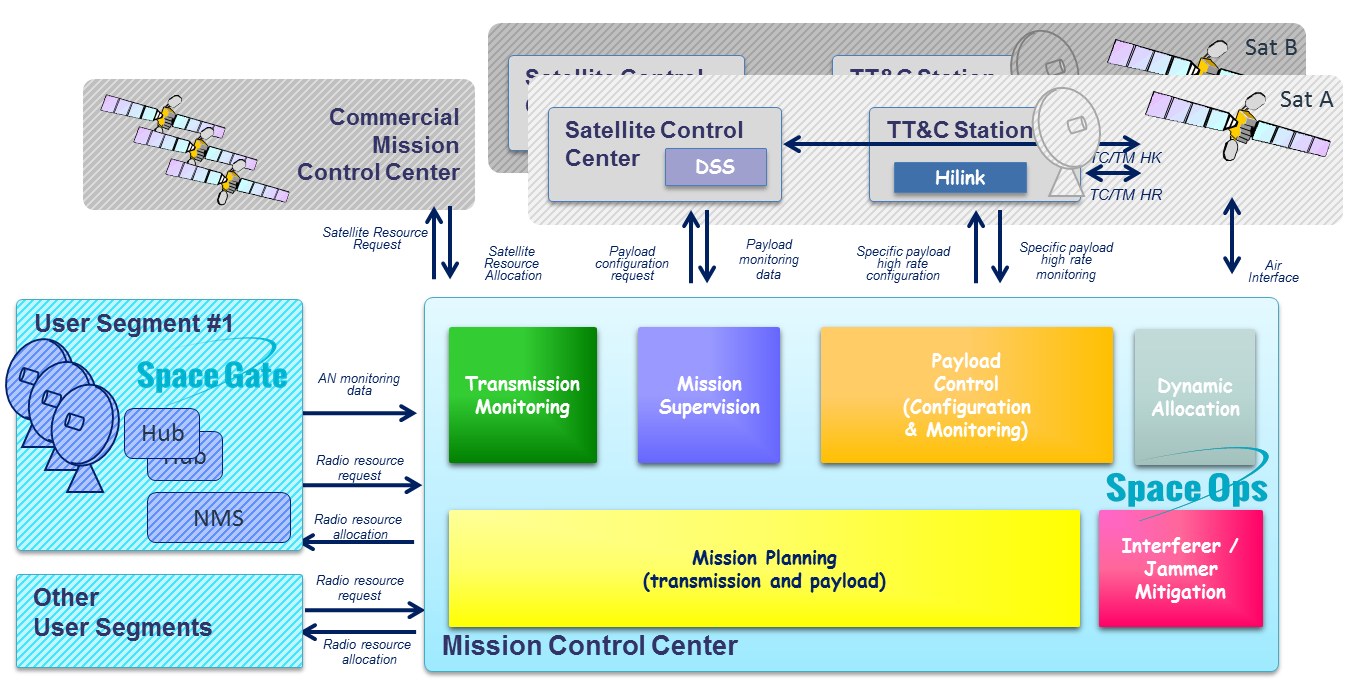
SpaceOps supports efficiently payload operations with different functionalities:
- Mission and Traffic planning: based on powerful algorithms to find out solutions to fit at best the communications needs to the payload resources
- Payload Control & Monitoring: to operate the payload and interface with Satellite Control Centre (SCC)
- Spectrum Monitoring: especially useful to monitor multi-spot payloads, and detect potential spectrum issues such as interference and jamming
- Interference / jamming mitigation: based on ground and/or payload mechanisms
- Mission Supervision: to provide an high level and all-encompassing view to easily monitor the complete mission segment.
The following figure illustrates SpaceOps position in the landscape of a complex satellite system including several satellites, allowing to manage commercial satellites resources and implementing several user segments.
The overall product development approach is performed according to an iterative and agile process. It avoids the tunnel effect frequently observed in complex software products development.
The development lifecycle relies on the following sequence :
- Incubation phase: includes the finalization of the specification and the product functional architecture definition. The incubation phase ends with the Preliminary Design Review (MS PDR).
- Incremental phase: allows to develop the product by version. Each sprint incorporates detailed definition (stories) of what has to be implemented, and validated. Therefore the maturity of the design and the Software developments are done by increments. This phase is closed by the Final Design Review (MS FDR).
- Validation phase: when a release composed of several sprints has been tested and is available, it is provided to the System Integration Verification & Validation (IVV) team for further testing. Then a verification phase is performed with the target Mission Segment customization.
The project is currently right in the middle of its incubation phase where all the User Requirements and Use Cases identified to fit at best commercial market needs are being processed to orient the new features developments and prioritise them.
Aside these engineering and development scheduling activities, an IVV pull strategy is also under definition.




